The full form of GST is GOODS AND SERVICE TAX.
GST is a Value Added Tax, a Continuous Chain of TAX, the Burden is borne by the final consumer and there is No cascading of Taxes.
What is GST?
The full form of GST is GOODS AND SERVICE TAX. The Incidence of tax is shifted to the other person, it is regressive in nature.
What is the Threshold Limit?
Threshold limit is Rs.10Lacs limit for both Goods & Services in the states such as Tripura, Nagaland, Mizoram, Manipur.
20 Lacs threshold Limit for both Goods & Services in States like Sikkim, Uttarakhand, Puducherry, Meghalaya, Arunanchal Pradesh, Telangana. 20Lacs threshold limit for Services and 40Lacs limit for Goods, in all other states including Jammu & Kashmir, Assam & Himachal Pradesh.
What are the types of Taxes in GST?
Sale within the State -CGST & SGST are applicable,For inter State Sales IGST,For Sales within Union Territory UTGST

The government spends money on public expenditure and for welfare and economic growth of the country, collected from citizens of the country.
A person who pays GST doesn’t even feel its impact. It doesn’t pinch you.
Tax is a burden, it is not a voluntary payment, it is collected through legislative authority. It is an enforced contribution.
There are two types of taxes-
Direct taxes-The Incidence of tax is borne directly by you on your income, it is progressive in nature. Example, Income tax, corporate tax, Agricultural Tax
Indirect taxes-The Incidence of tax is shifted to the other person, it is regressive in nature. Example, GST & Custom Duty
Tax on Tax is Surcharge & Cess
CGST(Central Goods and Service Tax) has merged all Pre-GST taxes such as Excise Duty, Service Tax, Surcharge & Cess
SGST(State Goods and Service Tax) has merged all Pre-GST Taxes such as Purchase Tax, VAT, Luxury Tax, Entry Tax, Surcharge & Cess
IGST(Integrated Goods and Service Tax ) has merged all Pre-GST taxes such as Central Sales Tax, Countervailing Duty, Special Additional Duty

Exemptions- All goods and services are taxable, except a few which are excluded from GST, and some which are taxable are exempted .
Seamless flow of credit- Credit is available seamlessly.
CGST ITC credit is first used for setoff against CGST output, then for IGST.
SGST ITC credit is first used for setoff against SGST output, then for IGST.
IGST ITC credit first use for IGST output, Then for CGST and balance for SGST.
One common service portal is used across the Country for all registrations, Payment of GST, Return Filing, Generation of E way Bills, Claiming refunds, etc under the direct control of GST council members.
GST is not leviable on
| Alcoholic Liquor for human consumption on which State Excise is leviable. | Petroleum Crude, diesel, Petrol ATF, Natural Gas on which Central Excise Duty and VAT,CST is leviable. | Tobacco on which Central Excise Duty and GST is leviable. | Opium, Narcotic drugs on which State Excise and GST is leviable | Immovable Property eg. Land |
Features of GST-
GST is an important source of revenue, Tax Incidence is shifted to the other Person, It is a Tax on Goods & Services, No direct pinch(included in the price of goods), increases the price of goods, Wider tax base, Promotes social welfare by increasing GST on sin goods to discourage buying, it is regressive in nature.
Evolution of GST-
Vajpayee Government started discussing about introduction of GST in 2000 and finally GST came into force on 01.07.2017 (including J&K on 08.07.2017).
GST is also called VAT(Value Added Tax) in many countries. GST is followed in more than 160+ countries. Brazil, Canada and India follow dual GST concept, where state and centre both get their share.
Compensation Cees
is in addition to the normal GST collected on certain goods like Aerated Beverages, Cars, tobacco, which is reimbursed by the center to the states for the losses incurred by the States.
Cascading effect is a Tax on Tax , which is reduced in GST era. GST is consumption based tax.
GST rates for goods are different across categories as per classification in Schedule II, as same GST rates can’t apply to different items due to their utility and consumption patterns such as notebooks, cars, restaurants, bikes.
If you are registered and cross the threshold limit, you have to collect and Pay GST.
On agricultural products, no GST is charged, except a few agricultural products on which there is reverse charge mechanism , where the buyer pays GST instead of the seller. If some packaging, processing happening on the agricultural goods, then GST is charged.
Pre-GST Era–
There was No credit of CENVAT and No setoff of CENVAT (Excise Duty on Manufacturing- Center Tax) against VAT(State tax for Goods) or vice versa, Non integration of Vat and Service Tax eg, CA firm was not able to claim credit of VAT paid on Laptop’s purchased, Non inclusion of local taxes with State VAT, Non integration of CST and VAT and no CENVAT for movement of goods inter state.
Framework of GST–
Center GST, State GST, Union Territory GST, Integrated GST
Integrated GST is a mechanism for adjusted Credit.
Location of Supplier and Place of Supply determines whether CGST, SGST, UTGST or IGST is applicable.
UTGST is like states. If trading to and from Union Territory or Union Territory States, CGST+UTGST applies.
If Trading interstate from or to Union Territory States, IGST is applicable.
There are Five Union Territories, governed by the President of India such as Andaman Nicobar, Lakshwadeep, Ladakh, Dadra & Nagra Haveli and Daman & Diu, Chandigarh) + Three more Union Territory States having their own legislature, own separate ACTS such as Delhi, Jammu & Kashmir & Puducherry)
Harmonized System of nomenclature used across the globe for Goods.
Service Accounting code is followed for Services.
Central GST Rates- 0%,1.125%,1.5%,2.5%,6%,9%,14%
State GST Rates- 0%,1.125%,1.5%,2.5%,6%,9%,14%

Taxable person is a person who crosses the threshold limit, whether registered or not, whether registered voluntarily or who is liable for registration. Once registered , all the provisions of the act will be applicable to you.
Forward charge v/s RCM
| Forward charge | RCM | |
| Who will pay GST tax to the government | Supplier | Receiver |
NRI on a visit to India for business is a Casual taxable payer, have to register for GST and pay GST.
Registration-
Why registration?
GST registration enables Identification of tax payer and makes the registered person GST compliant.
It legally recognize a person as a supplier who then collects tax and can claim any credit of tax paid on Purchases ie, Input Tax Credits.
Voluntary or compulsory registration?
Once you are registered, you are liable to collect tax .
If you are not registered but liable to register, then you have to pay GST from your own pocket , you can’t collect GST from the customers.
Seamless flow of credit.
Registration is PAN based, one registration for all taxes, that is one registration for CGST,SGST,IGST and UTGST
No centralized registration, registration is for each state or Union Territory.
Register in every state from where you make a taxable supply.
Aggregate turnover has to be calculated on all India basis
Branches within a state, multiple branches with single registration within a state is sufficient.
Multiple places of business may be granted separate registration for each such place.
Taxable person is a person who is registered or liable to register.
Registrations –
sec 22-person liable to register – if you are making taxable supply and where aggregate Turnover is more than the threshold limit, you are liable to register under GST. Turnover on your own account is to be included and not belonging to others.
sec 23-person not liable to register- IF you are exclusively into exempt goods or services or both or not liable to pay tax such as petroleum products, running a charitable trust, or an agriculturist for cultivation of land by oneself or your family member, having interstate supply of service up to Rs.20lacs or Rs.10lacs In Tripura, Nagaland, Manipur & MIzoram, notified handicraft, only Reverse Charge Mechanism, supply by Goods Transport Agency to Private Company, are a casual taxable person, or a commission agent for purchase, sale of agricultural produce.
sec 24-compulsory registration is for all taxable goods or services or both, if you cross threshold limit and satisfy other conditions.
sec 25-proceduer for registration –
You can apply for UIN number, if you have made only purchases on which GST is paid, and you are not a taxable person, not a registered person, and can claim refund of GST paid accordingly.
sec 26-Demed registration
sec 27-casual taxable person or Non Resident provisions- has no fixed place of business in any state or in India, has to take registration in a state from where you want to do business, no composition, no centralized scheme for both.
Within 30 days from date of becoming liable for registration
If opted for regular, then no composition scheme, one registration per state , obtain separate registration in Reg 01 for each distinct place of business.
Voluntary registration
Distinct person – PAN is compulsory , except Non Resident who can apply through TAN, UIN number for claiming refund, no return, centralised UIN , UIN number is issued within 3 working days.
Suo moto registration -on his own account
sec 28-amanedment of registration- core fields or non-core fields are done on GST portal or through GST officer.
sec 29-cancellation or surrender of registration-
cancellation-by the taxpayer, by officer, by legal heirs
surrender-when application is made for cancellation of registration, whether by taxable person or by department, it take some time to cancel, so during this period , proper officer may suspend the registration.- no return needs to be filed during this period , no payment is to be made.
What is the Threshold Limit?
Threshold limit is Rs.10Lacs limit for both Goods & Services in the states such as Tripura, Nagaland, Mizoram, Manipur
20 Lacs threshold Limit for both Goods & Services in States like Sikkim, Uttarakhand, Puducherry, Meghalaya, Arunanchal Pradesh, Telangana
20Lacs threshold limit for Services and 40Lacs limit for Goods, in all other states including Jammu & Kashmir, Assam & Himachal Pradesh.
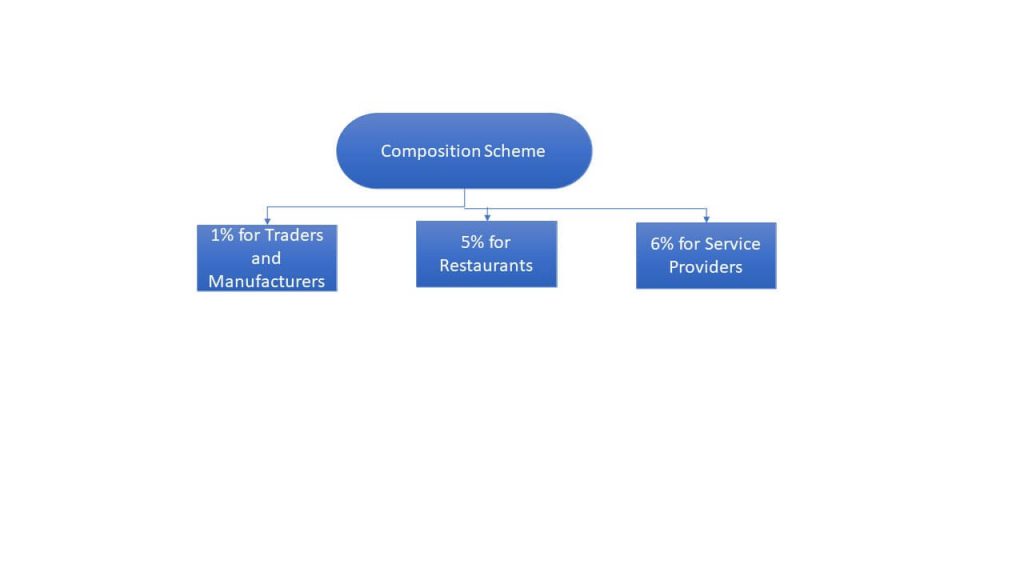
Composition Scheme
GST rate is 1% for manufacturing & trading, 5% for restaurant services having Turnover up to Rs.1.5crores and 6% for other small service providers. This scheme is only for intra state sales and no Input Tax Credit can be claimed.
Relaxation in tax compliances and provides lower taxes.
If you have turnover from the supply of goods being a trader, manufacturer or restaurants below a threshold limit of turnover of Rs.1.5crores or supply of service below Rs.50Lacs, in the preceding financial year, you can opt for a composition scheme in the current year.
It is the voluntary and optional scheme, quarterly payment of taxes, at specified rates without claiming ITC. One annual return, No export allowed, No interstate sales allowed.
Inter-state purchases is allowed. But inter-state sales is not allowed.
Tax is applicable under regular GST only once you cross Rs.1.5 crores, as a trader, manufacturer or restaurant. Not on turnover up to Rs.1.5 crores.
Once composition scheme is followed in one branch, you fall under composition scheme for all branches.
You can issue bill of supply, not an invoice, in case of composition scheme, because you can’t charge GST from the customer.
Before the beginning of every year, u can opt in or opt out of the composition scheme.
The turnover of all states are taken together for each PAN irrespective of different GST numbers to calculate the threshold benefit.
10(1) & 10(2) is for goods and services. You, as a trader can deal in Goods with 10% limit for providing services up to a threshold limit of Rs.1.5 crores.
10(2A) can’t supply goods and services. It is only applicable for services with Threshold limit of up to Rs.50 lacs
10(1) GST @1%- manufacturer & trader. Threshold limit is Rs.1.5crores.
Tripura ,Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram, Sikkim, Uttarakhand, Meghalaya, Arunanchal Pradesh is Rs.75lacs.
Once u are operating in Tripura, Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram, Sikkim, Uttarakhand, Meghalaya, Arunanchal Pradesh, then your total turnover limit is Rs.75 lacs.
10(2)GST @5%- Restaurant service provider. Threshold limit is Rs.1.5crores.
10(2A)GST @6%- Other small service provider. Threshold limit is Rs.50lacs.
NO ITC, no Inter-state sales, no GST on invoice, You have to pay GST from pocket, No credit of ITC if someone purchases from a composition dealer, It breaks the chain of ITC.
Not much compliance.
Restaurant can’t claim ITC even in regular registration. For restaurants, GST rate under regular and composition scheme is same 5%.
Benefits of GST–
Unified GST, Boost exports, encourages manufacturing, Encourages employment, Simplified tax structure, harmonization of tax, common system of classification of goods & services, no interaction with department due to common GST portal, automated system , ease of doing business, no multiple books due to single place records for all ledgers, reduce the price increase profits, zero rated supplies gets refund, exemptions, composition scheme for small taxpayers.
Ultra virus– Crossing your limits. No tax should be levied or collected except by the authority of law.
Levy-Imposition of Tax
There are Four ingredients to levy tax-
Event– Supply of Goods or Services.
Tax Measure-Value of The goods or Services .
Rate of Tax-As per Rate Schedule for Goods or service.
Person who shall pay-Supplier, Service Provider, Service Receiver, E commerce Operator.
246A-Special Powers to both Center and State to frame laws for GST.
269A-IGST and inter state laws for credit distribution to be divided between both center and state.
279A-GST council members comprise of Finance Minister from the center, One from state, One member each from each state, 50% quorum required, 1/3rd voting power with center and 2/3 rd with states to make respective amendments.
